About the Speaker: Roshan Yedery develops and serves as team manager and leader for Innovation Management activities & programs for Venture Center including IPFACE. He has 6 years of work experience in IP management and commercialization and is a Ph.D. in Biochemistry from National Institute of Research in Reproductive Health, Mumbai. Additionally, he has certificate courses in Technology Transfer, Foundation for Advanced Education in the Sciences, NIH, Bethesda, U.S.A and in Research Commercialization, National Council of Entrepreneurial Tech Transfer, Washington DC, U.S.A.
Intellectual Property rights
Intellectual property (IP) refers to creations of the mind, such as inventions; literary and artistic works; designs; and symbols, names and images used in commerce. IP is protected in law by, for example, patents, copy right and trademarks, which enable people to earn recognition or financial benefit from what they invent or create. By striking the right balance between the interests of innovators and the wider public interest, the IP system aims to foster an environment in which creativity and innovation can flourish [1].
Types of IP
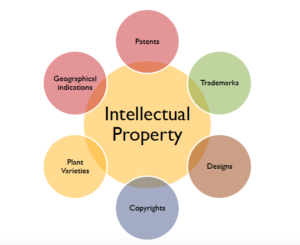
1. Patents:
A patent in the law is a property right and hence, can be gifted, inherited, assigned, sold or licensed. The patent right is territorial in nature and inventors/their assignees will have to file separate patent applications in countries of their interest, along with necessary fees, for obtaining patents in those countries [2].
2. Trademarks
Popularly known as brand name in layman’s language, is a visual symbol which may be a word signature, name, device, label, numerals or combination of colours used by one undertaking on goods or services or other articles of commerce to distinguish it from other similar goods or services originating from a different undertaking [3].
3. Designs
Design means the features of shape, configuration, pattern or ornament or composition of lines or colour or combination thereof applied to any article whether two dimensional or three dimensional or in both forms, by any industrial process or means, whether manual, mechanical or chemical, separate or combined [4].
4. Copyrights
Copyright is a right given by the law to creators of literary, dramatic, musical and artistic works and producers of cinematograph films and sound recordings. It is a bundle of rights including, interalia, rights of reproduction, communication to the public, adaptation, and translation of the work [5].
5. Geographical Indications
A geographical indication (GI) is a sign used on products that have a specific geographical origin and possess qualities or a reputation that are due to that origin [6].
6. Plant Varieties
To accelerate agricultural development, it is necessary to protect plants breeders’ rights to stimulate investment for research and development for the development of new plant varieties. Simultaneously, it is helpful for the seed industry to ensure availability of high quality of seeds to the farmers [7].
About the Author: Shubham Singh is presently working as the BIRAC Social Innovator at Venture Center, Pune.
References:
[1] http://www.wipo.int/about-ip/en/
[2] http://www.pfc.org.in/faqpat.htm
[3] http://www.ipindia.nic.in/faq-tm.htm
[4] http://www.heerlaw.com/industrial-design-basics-benefits
[5] http://copyright.gov.in/frmfaq.aspx
[6] http://www.ipindia.nic.in/faq-gi.htm
[7] http://plantauthority.gov.in/faq’s.htm

