Efficient immune signalling response against pathogens is crucial for resolving infections. However, many pathogens thrive by evolving strategies to evade the host immune response. Scientists at NCCS are exploring ways to rewire immune signaling pathways or networks by using synthetic signaling circuits. Using principles of network biology, they are understanding the dynamics of the pathogen/ disease thereby developing therapies that manipulate host’s natural system probed by a synthetic device to fight the pathogen. They are currently focused on developing therapeutic strategies to treat Leishmaniasis. Leishmania parasite infects host by disrupting many important immune signaling pathways within immune cells namely macrophages.
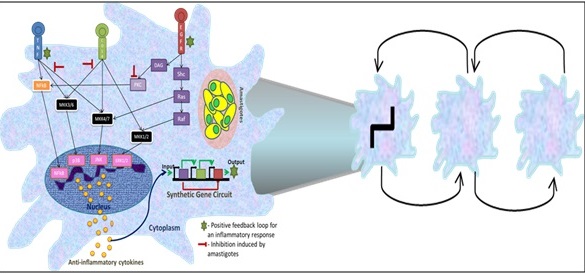 Figure 1: Intervention of cross-talk points by synthetic circuit for immune modulation in Leishmaniasis.
Figure 1: Intervention of cross-talk points by synthetic circuit for immune modulation in Leishmaniasis.
Potential application of this research is in developing synthetic signaling circuits as therapeutics for infectious diseases.
Uploads: Poster on Immune Modulation using Synthetic Signaling Circuit in Leishmaniasis
Reference:
- Immune signal transduction in leishmaniasis from natural to artificial systems: role of feedback loop insertion, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects, 2014, 1840(1), pp.71-79 (Article).
- Subversion mechanisms by which Leishmania parasites can escape the host immune response: a signaling point of view, Clinical microbiology reviews, 2005, 18(2), pp.293-305 (Article).
Technology Readiness: TRL B1/ B2
Technology Status: Proprietary Know-how
Technology Availability: Know-how available for co-development and/or sponsored projects.
